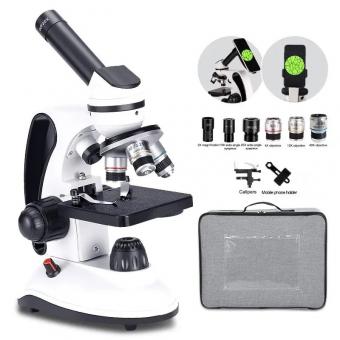
What Does A Light Microscope Do ?
A light microscope is an optical instrument that uses visible light to magnify and observe small objects or organisms. It works by passing light through a specimen and then through a series of lenses that magnify the image. The magnified image can be observed directly through the eyepiece or captured using a camera. Light microscopes are commonly used in various scientific fields, such as biology, medicine, and materials science, to study the structure and behavior of cells, tissues, and other microscopic samples. They have a range of magnification levels, typically up to around 1000x, allowing researchers to visualize details that are not visible to the naked eye.
1、 Magnification: Enlarges the image of small objects for better visibility.
A light microscope is a scientific instrument that uses visible light to magnify small objects for better visibility. It is one of the most commonly used tools in biology and other scientific fields. The primary function of a light microscope is to magnify the image of small objects, allowing scientists to observe and study them in detail.
Magnification is the key feature of a light microscope. It enlarges the image of the specimen, making it easier to see and analyze. By increasing the size of the object, scientists can observe its structure, shape, and other characteristics that may not be visible to the naked eye. This enables them to study the intricate details of cells, tissues, and other microscopic organisms.
In addition to magnification, light microscopes also have other important features. They often have adjustable lenses, allowing scientists to focus on different layers of the specimen. This helps in obtaining clear and sharp images. Some microscopes also have built-in lighting systems, such as brightfield or phase contrast illumination, which enhance the visibility of the specimen.
It is worth mentioning that light microscopes have evolved over time, and newer technologies have been incorporated to improve their capabilities. For example, the development of fluorescence microscopy has allowed scientists to label specific molecules or structures with fluorescent dyes, making them easier to visualize. Confocal microscopy, on the other hand, uses a laser to scan the specimen in thin sections, resulting in high-resolution three-dimensional images.
In conclusion, a light microscope is a powerful tool that magnifies small objects for better visibility. Its primary function is to enlarge the image of the specimen, allowing scientists to study its structure and characteristics in detail. With advancements in technology, light microscopes have become even more versatile and capable of providing valuable insights into the microscopic world.

2、 Resolution: Determines the level of detail that can be observed.
A light microscope is a powerful tool used in scientific research and medical diagnostics to observe and study microscopic objects. It works by using visible light to illuminate the specimen and magnify it, allowing scientists to see details that are not visible to the naked eye.
One of the key functions of a light microscope is resolution, which determines the level of detail that can be observed. Resolution refers to the ability of the microscope to distinguish between two closely spaced objects as separate entities. The higher the resolution, the clearer and more detailed the image will be. This is crucial in scientific research as it allows scientists to study the structure and function of cells, tissues, and microorganisms.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in light microscopy techniques, leading to improved resolution and image quality. Techniques such as confocal microscopy, which uses laser scanning to eliminate out-of-focus light, and super-resolution microscopy, which surpasses the diffraction limit of light, have revolutionized the field. These advancements have enabled scientists to observe cellular processes at the molecular level and gain a deeper understanding of biological systems.
Furthermore, the development of digital imaging technology has allowed for the capture and analysis of microscope images with high precision and accuracy. This has facilitated the integration of microscopy with other scientific disciplines, such as computer science and data analysis, leading to the emergence of fields like computational microscopy and image analysis.
In conclusion, a light microscope is a versatile tool that plays a crucial role in scientific research and medical diagnostics. Its ability to provide high-resolution images allows scientists to explore the microscopic world and unravel the mysteries of life. With ongoing advancements in technology, the capabilities of light microscopy continue to expand, opening up new avenues for scientific discovery.

3、 Illumination: Provides light to illuminate the specimen being observed.
A light microscope is a powerful tool used in scientific research and medical diagnostics to observe and study microscopic organisms and structures. It utilizes visible light to illuminate the specimen being observed, allowing scientists to visualize and analyze its characteristics and behavior.
Illumination is a crucial function of a light microscope as it provides the necessary light source to enhance the contrast and visibility of the specimen. By shining light onto the specimen, the microscope allows scientists to observe its intricate details and structures that would otherwise be invisible to the naked eye. The light source can be either transmitted through the specimen from below (transmitted light microscopy) or reflected off the specimen from above (reflected light microscopy).
In addition to illumination, a light microscope also includes other essential components such as lenses, objectives, and eyepieces. These components work together to magnify the image of the specimen, allowing scientists to observe it at various levels of magnification. The lenses and objectives help focus the light and create a clear and magnified image, while the eyepieces enable the observer to view and analyze the specimen comfortably.
With advancements in technology, light microscopes have evolved to offer higher resolution and improved imaging capabilities. Modern light microscopes often incorporate features such as phase contrast, fluorescence, and confocal microscopy, which further enhance the visualization and analysis of specimens. These advancements have revolutionized various fields of science, including biology, medicine, and materials science, enabling researchers to explore and understand the microscopic world in greater detail.
In conclusion, a light microscope primarily functions by providing illumination to the specimen being observed. This illumination, combined with other components, allows scientists to magnify and visualize microscopic structures, leading to significant advancements in scientific research and medical diagnostics.

4、 Objective lenses: Different lenses with varying magnification powers.
A light microscope is a scientific instrument that uses visible light to magnify and observe small objects or organisms that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. It consists of several components, including an eyepiece, a stage, a light source, and objective lenses.
Objective lenses are one of the most important components of a light microscope. They are responsible for magnifying the specimen being observed. Different objective lenses have varying magnification powers, allowing scientists to view the specimen at different levels of detail. Common magnification powers range from 4x to 100x, with some microscopes even capable of reaching higher magnifications.
The objective lenses are typically mounted on a rotating nosepiece, allowing the user to easily switch between different magnifications. By adjusting the focus and changing the objective lens, scientists can explore the specimen at different levels of magnification, revealing finer details and structures.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated objective lenses. These lenses are designed to provide higher resolution and better image quality. Some objective lenses also incorporate additional features such as phase contrast or fluorescence capabilities, allowing scientists to study specific structures or processes within the specimen.
Overall, objective lenses play a crucial role in the functionality of a light microscope. They allow scientists to observe and study microscopic objects with greater clarity and detail, contributing to our understanding of the microscopic world and its impact on various scientific disciplines.