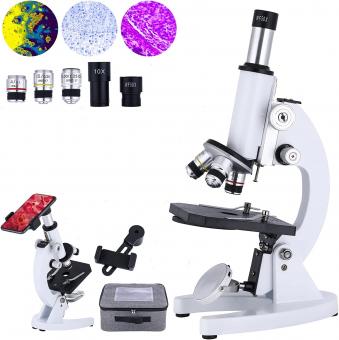
What Does An Electron Microscope Look Like ?
An electron microscope is a complex scientific instrument that is designed to magnify objects at a much higher resolution than a traditional light microscope. It typically consists of a vacuum chamber, an electron gun, a series of electromagnetic lenses, and a detector. The electron gun produces a beam of electrons that is focused and directed onto the sample by the lenses. The detector then collects the electrons that have interacted with the sample and produces an image that can be viewed on a screen or recorded for further analysis. Electron microscopes come in various sizes and configurations, ranging from tabletop models to large, multi-million dollar instruments used in research laboratories.
1、 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that uses a focused beam of electrons to create high-resolution images of a sample's surface. The SEM is a large, complex instrument that typically consists of a vacuum chamber, electron gun, electron lenses, and a detector.
The vacuum chamber is necessary to prevent the electrons from interacting with air molecules, which would scatter the beam and degrade the image quality. The electron gun produces a beam of electrons that is focused by a series of lenses onto the sample. The detector collects the electrons that are scattered or emitted from the sample and converts them into an image.
The SEM is capable of producing images with a resolution of a few nanometers, which is much higher than that of a light microscope. This makes it an invaluable tool for studying the structure and composition of materials at the nanoscale.
In recent years, advances in SEM technology have led to the development of new techniques such as electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). These techniques allow researchers to obtain additional information about the sample's crystal structure and chemical composition, respectively.
Overall, the SEM is a powerful tool for investigating the properties of materials at the nanoscale, and its continued development is likely to lead to new discoveries and applications in fields such as materials science, biology, and electronics.

2、 Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
A Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) is a type of electron microscope that uses a beam of electrons to create an image of a sample. The TEM is a large, complex instrument that consists of several components, including an electron gun, a series of electromagnetic lenses, and a detector.
The electron gun produces a beam of electrons that is focused by the lenses onto the sample. As the electrons pass through the sample, they interact with the atoms and molecules, producing a signal that is detected by the detector. This signal is then used to create an image of the sample.
The TEM is a highly specialized instrument that is used in a variety of scientific fields, including materials science, biology, and physics. It is capable of producing images with a resolution of less than 0.1 nanometers, which is several orders of magnitude better than the resolution of a light microscope.
In terms of appearance, a TEM is a large, box-like instrument that is typically several meters long. It is housed in a specially designed room that is free from vibrations and electromagnetic interference. The instrument is operated by highly trained technicians and scientists who are skilled in the use of electron microscopy techniques.
In recent years, there have been significant advances in the field of electron microscopy, including the development of new techniques such as cryo-electron microscopy, which allows for the imaging of biological samples in their native state. These advances have opened up new avenues of research and are helping to advance our understanding of the world around us.

3、 Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM)
A Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM) is a type of electron microscope that uses a focused beam of electrons to create high-resolution images of a sample. The STEM is similar in appearance to a traditional transmission electron microscope (TEM), but it has additional components that allow it to scan the sample and create images with higher resolution.
The STEM consists of a vacuum chamber, an electron gun, a series of lenses to focus the electron beam, and a detector to capture the electrons that pass through the sample. The sample is mounted on a stage that can be moved in three dimensions to allow for precise positioning of the sample under the electron beam.
The STEM is capable of producing images with a resolution of a few picometers, which is several orders of magnitude better than the resolution of a traditional light microscope. This high resolution allows researchers to study the structure and composition of materials at the atomic level.
Recent advances in STEM technology have allowed for the development of aberration-corrected STEMs, which can produce even higher resolution images by correcting for distortions in the electron beam. These instruments are being used to study a wide range of materials, from biological samples to advanced materials for electronics and energy storage.

4、 Reflection Electron Microscope (REM)
"What does an electron microscope look like?" An electron microscope is a scientific instrument that uses a beam of electrons to magnify and visualize objects that are too small to be seen with a traditional light microscope. Electron microscopes come in different shapes and sizes, but they all have a similar basic design. They consist of a vacuum chamber, an electron gun, a series of electromagnetic lenses, and a detector.
The electron gun produces a beam of electrons that is focused and directed by the electromagnetic lenses onto the sample being studied. The detector collects the electrons that have interacted with the sample and produces an image that can be viewed on a screen or recorded for later analysis.
One type of electron microscope is the Reflection Electron Microscope (REM). This type of microscope uses a beam of electrons that is reflected off the surface of the sample being studied. The reflected electrons are then collected by a detector and used to produce an image of the sample.
The latest point of view on electron microscopes is that they have revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world. They have allowed scientists to study the structure and function of cells, molecules, and materials at an unprecedented level of detail. With advances in technology, electron microscopes are becoming more powerful and versatile, allowing researchers to explore new frontiers in science and engineering.