What Is A Neutral Density Filter In Photography?
A neutral density filter in photography is a filter that reduces the amount of light entering the camera without affecting the color of the image. It allows photographers to use slower shutter speeds or wider apertures in bright conditions, giving them more control over exposure and depth of field. This type of filter is particularly useful for capturing long exposure shots in daylight or for achieving a shallow depth of field in bright light.
1、 Definition and Purpose

A neutral density filter in photography is a type of filter that reduces the amount of light entering the camera without affecting the color of the image. It is essentially a darkened piece of glass or resin that can be attached to the front of a camera lens.
The purpose of a neutral density filter is to allow photographers to achieve certain effects that would be difficult or impossible to achieve without it. One of the main uses of a neutral density filter is to enable longer exposure times in bright conditions, such as when photographing waterfalls or rivers, to create a smooth, flowing effect. It can also be used to achieve a shallower depth of field in bright light, allowing for more creative control over the focus of the image.
From the latest point of view, neutral density filters are also used in videography to maintain a consistent shutter speed and frame rate in bright conditions, resulting in smoother and more professional-looking footage. Additionally, they are used in astrophotography to capture long-exposure shots of the night sky without overexposing the image.
In summary, a neutral density filter in photography is a versatile tool that allows photographers to control the amount of light entering the camera, enabling them to achieve creative effects and maintain consistent exposure in various shooting conditions.
2、 Types and Variations

A neutral density filter in photography is a type of filter that reduces the amount of light entering the camera without affecting the color of the image. It is essentially a darkened piece of glass or resin that can be attached to the front of a camera lens. This reduction in light allows photographers to use slower shutter speeds or wider apertures in bright conditions, enabling creative effects such as motion blur or shallow depth of field.
Types and Variations:
1. Solid Neutral Density Filters: These filters provide a consistent reduction in light across the entire image, allowing for greater control over exposure settings.
2. Graduated Neutral Density Filters: These filters have a gradient of darkness, with one half being clear and the other half gradually becoming darker. They are often used to balance the exposure between a bright sky and a darker foreground in landscape photography.
The latest point of view on neutral density filters in photography emphasizes their continued relevance in the digital age. While modern cameras offer a wide dynamic range and advanced exposure control, neutral density filters remain valuable tools for achieving specific creative effects in-camera. Additionally, advancements in filter technology have led to the development of high-quality, multi-coated filters that minimize reflections and maintain image clarity. As a result, neutral density filters continue to be popular among photographers seeking to expand their creative possibilities and achieve precise exposure control in challenging lighting conditions.
3、 Optical Characteristics
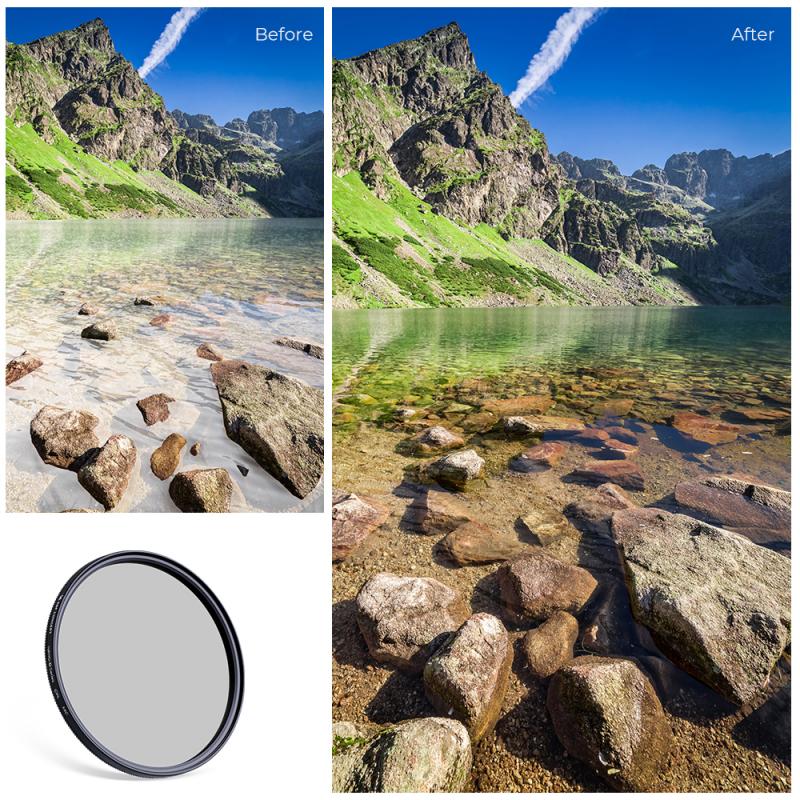

A neutral density filter in photography is a type of filter that reduces the amount of light entering the camera lens without affecting the color or contrast of the image. This allows photographers to use longer exposure times or wider apertures in bright conditions, enabling creative effects such as motion blur in water or capturing the movement of clouds in the sky.
Optical Characteristics:
Neutral density filters are characterized by their ability to uniformly reduce the intensity of light across the entire visible spectrum. They are typically available in different strengths, measured in stops, to provide varying levels of light reduction. These filters are often made of high-quality optical glass or resin to ensure minimal impact on image quality.
Latest Point of View:
In recent years, neutral density filters have become increasingly popular among photographers seeking to achieve long exposure effects in their images. With the rise of social media platforms and the growing interest in landscape and travel photography, the use of neutral density filters has become more widespread. Additionally, advancements in filter technology have led to the development of high-quality, multi-coated filters that minimize reflections and flare, further enhancing image quality.
In conclusion, a neutral density filter in photography is a valuable tool for controlling exposure in bright conditions and achieving creative effects. Its optical characteristics allow photographers to maintain color and contrast while reducing light intensity, and the latest advancements in filter technology have made them more accessible and effective than ever before.
4、 Applications in Photography

A neutral density filter in photography is a type of filter that reduces the amount of light entering the camera without affecting the color of the image. It is essentially a darkened piece of glass or resin that can be attached to the front of a camera lens. The primary purpose of a neutral density filter is to allow photographers to use longer shutter speeds or wider apertures in bright conditions, without overexposing the image.
Applications in Photography:
1. Long Exposure Photography: Neutral density filters are commonly used in long exposure photography to create a sense of motion in water, clouds, or other moving subjects. By reducing the amount of light, the filter allows for longer exposure times without overexposing the image.
2. Portraiture: In portrait photography, neutral density filters can be used to achieve a shallow depth of field in bright conditions, allowing the photographer to blur the background while maintaining proper exposure on the subject.
3. Cinematography: Neutral density filters are widely used in filmmaking to control the exposure of the image, especially in outdoor settings where the light can be intense.
4. Time-lapse Photography: When capturing time-lapse sequences, neutral density filters can help maintain consistent exposure over a series of images taken over an extended period of time.
The latest point of view on neutral density filters in photography emphasizes their continued relevance in the digital age, as they provide photographers with greater creative control over exposure and depth of field, even in challenging lighting conditions. With advancements in filter technology, photographers now have access to a wide range of neutral density filters with varying strengths, allowing for more precise control over exposure levels. Additionally, the use of neutral density filters in combination with digital post-processing techniques has opened up new possibilities for creative expression in photography.