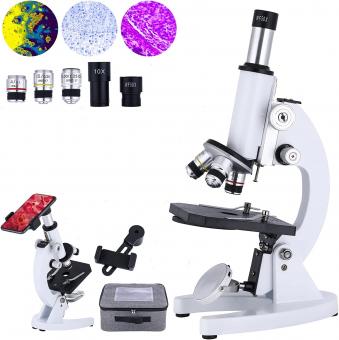
What Is The Illuminator On A Microscope ?
The illuminator on a microscope is a light source that provides illumination to the specimen being observed. It is typically located at the base of the microscope and can be either built-in or external. The illuminator emits light, which passes through the condenser and then through the specimen, allowing it to be magnified and observed through the objective lenses. The intensity and direction of the light can be adjusted to optimize the visibility and clarity of the specimen. Different types of illuminators, such as halogen bulbs or LED lights, may be used depending on the specific microscope model and application.
1、 Function and Purpose of the Illuminator in Microscopes
The illuminator on a microscope is a crucial component that provides the necessary light to illuminate the specimen being observed. It is typically located at the base of the microscope and consists of a light source, such as a halogen bulb or LED, along with a condenser lens system.
The main function of the illuminator is to provide a uniform and adjustable light source that allows for clear visualization of the specimen. By directing light onto the specimen, the illuminator enhances contrast and improves the visibility of fine details. It also helps to control the intensity and direction of the light, ensuring optimal illumination for different types of specimens and objectives.
The purpose of the illuminator is to enable the observer to see the specimen with sufficient brightness and clarity. It plays a crucial role in various microscopy techniques, including brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast, and fluorescence microscopy. Each technique requires specific lighting conditions, and the illuminator allows for the adjustment of light intensity and angle to achieve the desired effect.
In recent years, advancements in LED technology have revolutionized microscope illuminators. LED illuminators offer several advantages over traditional halogen bulbs, including longer lifespan, lower energy consumption, and improved color rendering. They also produce less heat, reducing the risk of specimen damage and making them more suitable for live cell imaging.
In conclusion, the illuminator on a microscope is an essential component that provides the necessary light to visualize specimens. It ensures optimal illumination and contrast, allowing for clear observation of fine details. With the advent of LED technology, illuminators have become more efficient and versatile, contributing to advancements in microscopy techniques.

2、 Types of Illuminators Used in Microscopy
The illuminator on a microscope is a crucial component that provides the necessary light to illuminate the specimen being observed. It plays a vital role in enhancing visibility and clarity during microscopic examination. The illuminator is responsible for producing a controlled and uniform light source that allows the user to observe the specimen with precision.
There are various types of illuminators used in microscopy, each with its own advantages and applications. One common type is the transmitted light illuminator, which is located beneath the stage of the microscope. It typically consists of a light source, such as a halogen bulb or an LED, and a condenser that focuses the light onto the specimen. Transmitted light illuminators are commonly used in brightfield microscopy, where the specimen is observed against a bright background.
Another type of illuminator is the reflected light illuminator, which is positioned above the stage. It directs light onto the specimen from above, allowing for the observation of opaque or reflective samples. Reflected light illuminators are commonly used in techniques such as darkfield microscopy, where the specimen appears bright against a dark background.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have led to the development of new illuminators. For instance, fluorescence microscopy utilizes specific illuminators that emit light at specific wavelengths to excite fluorescent molecules within the specimen. This enables the visualization of specific structures or molecules within the sample, providing valuable insights into cellular processes and interactions.
In conclusion, the illuminator on a microscope is a critical component that provides the necessary light to observe specimens. Different types of illuminators are used depending on the microscopy technique and the nature of the sample being examined. With ongoing advancements in microscopy technology, illuminators continue to evolve, enabling researchers to explore the microscopic world with greater precision and detail.

3、 Light Sources for Microscope Illumination
The illuminator on a microscope is a crucial component that provides the necessary light for observing specimens. It is responsible for illuminating the sample and enhancing visibility under the microscope. The illuminator can be found either above or below the stage, depending on the type of microscope.
In traditional microscopes, the illuminator is located below the stage and consists of a light source, such as a tungsten or halogen bulb, which emits light upwards through the condenser. The condenser then focuses and directs the light onto the specimen, making it easier to visualize. This type of illuminator is commonly used in brightfield microscopy, where the specimen appears darker against a bright background.
However, with advancements in technology, newer microscopes now often incorporate an illuminator located above the stage. These microscopes utilize LED (light-emitting diode) light sources, which offer several advantages over traditional bulbs. LEDs are more energy-efficient, have a longer lifespan, and emit less heat, reducing the risk of damaging delicate specimens. Additionally, LED illuminators can provide a more uniform and adjustable light intensity, allowing for better control and customization of the illumination.
Some microscopes also offer additional illumination techniques, such as phase contrast, fluorescence, or darkfield illumination. These techniques require specialized illuminators and optical components to enhance specific features or visualize certain types of samples.
In summary, the illuminator on a microscope is responsible for providing the necessary light to observe specimens. It can be located above or below the stage and may utilize traditional bulbs or LED light sources. The latest trend in microscope illuminators is the incorporation of LED technology, offering improved energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and better control over illumination.

4、 Adjusting and Controlling Illumination in Microscopes
The illuminator on a microscope is a crucial component that provides the necessary light to illuminate the specimen being observed. It is responsible for producing a bright and uniform light source, which is essential for achieving clear and detailed images under the microscope.
The illuminator is typically located at the base of the microscope and consists of a light source, such as a halogen bulb or an LED, along with various optical components to control and direct the light. The intensity of the light can be adjusted using a rheostat or a light intensity control knob, allowing the user to optimize the illumination for different specimens and magnifications.
Controlling the illumination is important because it directly affects the quality of the image. Insufficient illumination can result in dim and low-contrast images, making it difficult to observe fine details. On the other hand, excessive illumination can cause glare and overexposure, which can also degrade the image quality. Therefore, the illuminator allows the user to adjust the light intensity to achieve the optimal balance between brightness and contrast.
In recent years, advancements in microscope technology have led to the development of more sophisticated illuminators. For example, some microscopes now feature LED illuminators, which offer several advantages over traditional halogen bulbs. LEDs are more energy-efficient, have a longer lifespan, and can provide a more stable and consistent light source. Additionally, some LED illuminators allow for the adjustment of color temperature, enabling the user to fine-tune the lighting conditions for specific applications.
Overall, the illuminator plays a crucial role in microscopy by providing the necessary light to visualize specimens. The ability to adjust and control the illumination allows for optimal image quality and enhances the overall microscopy experience.