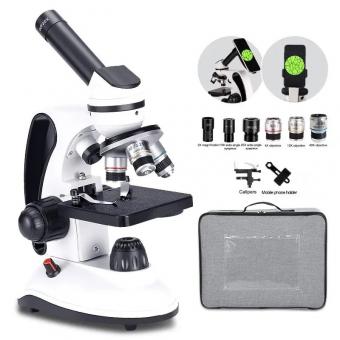
What Is The Total Magnification Of A Microscope ?
The total magnification of a microscope is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece lens.
1、 Objective lens magnification
The total magnification of a microscope refers to the overall level of enlargement achieved when viewing an object through the microscope. It is determined by the combined magnification of the objective lens and the eyepiece. The objective lens is responsible for the primary magnification, while the eyepiece further enlarges the image for the viewer.
The objective lens magnification is a crucial factor in determining the total magnification. Objective lenses come in various magnification powers, typically ranging from 4x to 100x or higher. The magnification power is usually indicated on the lens itself. For example, a 10x objective lens will magnify the object ten times its original size.
To calculate the total magnification, you multiply the magnification power of the objective lens by the magnification power of the eyepiece. The eyepiece typically has a fixed magnification of 10x. Therefore, if you are using a 10x objective lens and a 10x eyepiece, the total magnification would be 100x (10x objective lens magnification multiplied by 10x eyepiece magnification).
It is important to note that the total magnification is not the only factor that determines the quality of the image. Other factors, such as the numerical aperture of the lens and the resolution of the microscope, also play a significant role in the clarity and detail of the magnified image.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of microscopes with higher magnification capabilities. For example, some microscopes now offer objective lenses with magnification powers of 100x or even 1000x. These high magnification microscopes have revolutionized fields such as biology and medicine, allowing researchers to observe and study microscopic structures with unprecedented detail.
In conclusion, the total magnification of a microscope is determined by the combined magnification of the objective lens and the eyepiece. The objective lens magnification is the primary factor in determining the level of enlargement, while the eyepiece further enhances the image for the viewer. Advancements in technology have led to the development of microscopes with higher magnification capabilities, enabling researchers to explore the microscopic world with greater precision and detail.

2、 Eyepiece lens magnification
The total magnification of a microscope refers to the overall level of enlargement achieved when viewing an object through the microscope. It is determined by the combined magnification of the eyepiece lens and the objective lens. The eyepiece lens, also known as the ocular lens, is located at the top of the microscope and is the lens through which the viewer looks. The objective lens, on the other hand, is located at the bottom of the microscope and is responsible for gathering light and magnifying the image.
To calculate the total magnification of a microscope, you simply multiply the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of the objective lens. For example, if the eyepiece lens has a magnification of 10x and the objective lens has a magnification of 40x, the total magnification would be 400x (10x multiplied by 40x).
It is important to note that the total magnification of a microscope is not the only factor that determines the quality of the image. Other factors, such as the numerical aperture of the lenses and the resolution of the microscope, also play a significant role in the clarity and detail of the observed image.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of microscopes with higher magnification capabilities. Some modern microscopes can achieve total magnifications of up to 2000x or even higher. These high magnification microscopes are often used in specialized fields such as medical research, biology, and materials science, where the ability to observe fine details is crucial.
In conclusion, the total magnification of a microscope is determined by the combined magnification of the eyepiece lens and the objective lens. It is an important factor in determining the level of enlargement achieved when viewing an object through the microscope. With advancements in technology, microscopes with higher magnification capabilities have become available, allowing for more detailed observations in various scientific fields.

3、 Total magnification calculation
The total magnification of a microscope refers to the overall level of enlargement achieved when viewing an object through the microscope. It is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece.
The objective lens is responsible for the primary magnification and is available in various powers, typically ranging from 4x to 100x. The eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens, further magnifies the image produced by the objective lens. The standard magnification of an eyepiece is 10x.
To calculate the total magnification, you simply multiply the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. For example, if you are using a 40x objective lens and a 10x eyepiece, the total magnification would be 400x (40 x 10 = 400).
It is important to note that the total magnification is not the only factor that determines the quality of the image. Other factors such as the numerical aperture, resolution, and clarity of the lenses also play a significant role in the overall image quality.
In recent years, advancements in microscope technology have led to the development of high-powered microscopes capable of achieving even higher magnifications. These microscopes, such as electron microscopes, can achieve magnifications in the range of thousands or even millions of times. However, for most routine laboratory work and educational purposes, a total magnification of up to 1000x is typically sufficient.
In conclusion, the total magnification of a microscope is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. It is an important factor in determining the level of enlargement achieved when viewing objects through a microscope.

4、 Role of tube length in total magnification
The total magnification of a microscope refers to the overall level of enlargement achieved by the combination of the objective lens and the eyepiece. It is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. The objective lens is responsible for the primary magnification of the specimen, while the eyepiece further enlarges the image for the observer.
The magnification of the objective lens is determined by its focal length and the distance between the lens and the specimen. The eyepiece, on the other hand, typically has a fixed magnification power. By multiplying these two values together, the total magnification of the microscope is obtained.
Regarding the role of tube length in total magnification, it is important to note that the tube length refers to the distance between the objective lens and the eyepiece. Traditionally, microscopes have a standard tube length of 160 mm. However, some modern microscopes have a shorter tube length of 160 mm or even less.
The tube length affects the total magnification of the microscope because it influences the optical path length and the focal length of the objective lens. A shorter tube length can result in a higher total magnification because it reduces the distance between the objective lens and the eyepiece, allowing for a greater enlargement of the specimen.
However, it is essential to consider that changing the tube length can also affect other aspects of the microscope's performance, such as the field of view, depth of field, and image quality. Therefore, while a shorter tube length may increase the total magnification, it is crucial to balance it with other factors to ensure optimal imaging capabilities.
In conclusion, the total magnification of a microscope is determined by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. The tube length plays a role in total magnification by influencing the optical path length and focal length, but it is important to consider other factors to maintain overall image quality and performance.