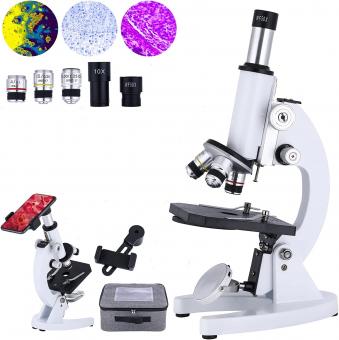
What Microscope Can Be Used To Examine Cells ?
A light microscope can be used to examine cells. This type of microscope uses visible light to illuminate the specimen and magnify it. Light microscopes can magnify up to 1000 times and are commonly used in biology labs to study cells and tissues. Other types of microscopes, such as electron microscopes, can also be used to examine cells, but they require more specialized equipment and expertise.
1、 Light Microscopy
Light microscopy is the most commonly used microscope to examine cells. It uses visible light to illuminate the sample and magnify the image. This type of microscope is versatile and can be used to examine a wide range of samples, including cells, tissues, and microorganisms. Light microscopy is also relatively easy to use and can provide high-resolution images of cells and their structures.
In recent years, advances in light microscopy have led to the development of new techniques that allow for even higher resolution imaging of cells. One such technique is called super-resolution microscopy, which uses fluorescent dyes and specialized optics to achieve resolutions beyond the diffraction limit of light. This technique has allowed researchers to study cellular structures and processes in unprecedented detail, revealing new insights into the workings of cells and their interactions with their environment.
Another recent development in light microscopy is the use of live-cell imaging, which allows researchers to observe cells in real-time as they carry out their functions. This technique has been particularly useful in studying dynamic processes such as cell division, migration, and signaling.
Overall, light microscopy remains the most widely used microscope for examining cells, and recent advances in the field have expanded its capabilities and allowed for even more detailed studies of cellular structures and processes.
2、 Fluorescence Microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy is a powerful tool that can be used to examine cells. This type of microscopy uses fluorescent dyes or proteins to label specific structures within cells, allowing them to be visualized under a microscope. Fluorescence microscopy has revolutionized the field of cell biology, allowing researchers to study the dynamics of cellular processes in real-time.
One of the key advantages of fluorescence microscopy is its ability to selectively label specific structures within cells. This allows researchers to study the function and behavior of individual components of cells, such as organelles, proteins, and DNA. Fluorescence microscopy can also be used to study the interactions between different components of cells, providing insights into the complex networks of molecular interactions that underlie cellular processes.
In recent years, advances in fluorescence microscopy have led to the development of new techniques that allow researchers to study cells in even greater detail. For example, super-resolution microscopy techniques such as STED and PALM have enabled researchers to visualize structures within cells at the nanoscale level. These techniques have opened up new avenues for research, allowing researchers to study the structure and function of cells in unprecedented detail.
Overall, fluorescence microscopy is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the field of cell biology. Its ability to selectively label specific structures within cells has allowed researchers to study the dynamics of cellular processes in real-time, providing insights into the complex networks of molecular interactions that underlie cellular function.

3、 Confocal Microscopy
Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool that can be used to examine cells. This type of microscopy uses a laser to scan a sample and create a three-dimensional image of the cells. Confocal microscopy is particularly useful for examining cells because it allows researchers to look at individual cells in great detail.
One of the advantages of confocal microscopy is that it can be used to examine cells in living organisms. This is important because it allows researchers to study cells in their natural environment, rather than in a laboratory setting. Confocal microscopy can also be used to examine cells in tissue samples, which can provide valuable information about the structure and function of cells in different parts of the body.
Another advantage of confocal microscopy is that it can be used to examine cells at high resolution. This means that researchers can see individual structures within cells, such as organelles and proteins. This level of detail can provide important insights into how cells function and how they are affected by disease.
Overall, confocal microscopy is an important tool for examining cells. It allows researchers to study cells in great detail, both in living organisms and in tissue samples. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that confocal microscopy will become even more powerful and useful for studying cells and understanding the complex processes that occur within them.

4、 Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) is a powerful tool that can be used to examine cells at the nanoscale level. TEM uses a beam of electrons to pass through a thin sample, allowing for high-resolution imaging of the internal structure of cells. This technique has been used extensively in cell biology research to study the ultrastructure of cells, including the arrangement of organelles, the structure of membranes, and the distribution of macromolecules.
Recent advances in TEM technology have further improved its capabilities for cell biology research. For example, cryo-TEM allows for the imaging of cells in their native, hydrated state, providing a more accurate representation of their structure and function. Additionally, correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) combines the high-resolution imaging of TEM with the specificity of fluorescence microscopy, allowing for the visualization of specific molecules within cells.
TEM has also been used to study the structure of viruses, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. By imaging the virus at high resolution, researchers have been able to better understand its structure and how it interacts with host cells, which has led to the development of new treatments and vaccines.
In summary, TEM is a powerful tool for examining cells at the nanoscale level, and recent advances in technology have further improved its capabilities for cell biology research.